| SVG 2 Requirement: | Consider allowing async/defer on 'script'. |
|---|---|
| Resolution: | SVG 2 will allow async/defer on 'script'. |
| Purpose: | To align with HTML. |
| Owner: | Cameron (ACTION-3280) |
| SVG 2 Requirement: | Incorporate SVG Tiny 1.2 script processing model. |
|---|---|
| Resolution: | SVG 2 will define how inline scriptable content will be processed, in a compatible way to HTML5 |
| Purpose: | To have consistent script running behavior across HTML and SVG. |
| Owner: | Cameron (ACTION-3282) |
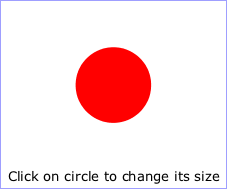
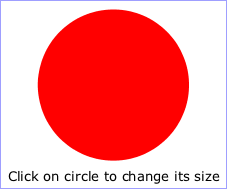
A 'script' element is equivalent to the 'script' element in HTML and thus is the place for scripts (e.g., ECMAScript). Any functions defined within any 'script' element have a "global" scope across the entire current document.
Example script01
defines a function circle_click which is called by the
'onclick' event attribute on the 'circle' element. The drawing
below on the left is the initial image. The drawing below on the right shows
the result after clicking on the circle.
Before attempting to execute the 'script' element the resolved media type value for 'script/type' must be inspected. If the SVG user agent does not support the scripting language then the 'script' element must not be executed.
]]>
  |
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
Attribute definitions:
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | content-type | application/ecmascript | no |
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| href | <url> | (none) | no |
Events can cause scripts to execute when either of the following has occurred:
Related sections of the spec:
The following event attributes are available on many SVG elements.
The complete list of events that are part of the SVG language and SVG DOM and descriptions of those events is provided in Complete list of supported events.
The contents of event attributes are always interpreted as ECMAScript, as if processed with the media type 'application/ecmascript'. [RFC2046][RFC4329]
Attribute definitions:
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| onload | <anything> | (none) | no |
Below are the definitions for the graphical event attributes. These can be specified on most graphics elements and container elements. (See the definition for each element to determine whether it can have a graphical event attribute specified on it.)
Note that 'svg/onload', defined above, is also classified as a graphical event attribute.
Attribute definitions:
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| onfocusin, onfocusout, onfocus, onblur, onclick, onkeydown, onkeyup, onmousedown, onmouseup, onmouseover, onmousemove, onmouseout | <anything> | (none) | no |
Below are the definitions for the document event attributes. These can be specified only on 'svg' elements.
The conformance class for the 'only-on-<svg> elements' criteria needs to be clarified here (this is for document validation presumably, so perhaps Conforming SVG Document Fragments would be appropriate to mention), the document event attributes should be fine to specify on any element, they just don't do much in all such cases, and it makes sense to not encourage uses where it doesn't have any real meaning. For Conforming Dynamic SVG Viewers: what the document event attributes should do is register an event listener for the event in question.
'onerror' should be available on image, script and elements that load external resources. This is related to issue 2254.
Attribute definitions:
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| onunload, onabort, onerror, onresize, onscroll, onzoom | <anything> | (none) | no |
Below are the definitions for the animation event attributes. These can be specified on the animation elements.
Attribute definitions:
| Name | Value | Lacuna value | Animatable |
|---|---|---|---|
| onbegin, onend, onrepeat | <anything> | (none) | no |
The SVGScriptElement interface corresponds to the 'script' element.
interface SVGScriptElement : SVGElement {
attribute DOMString type;
};
SVGScriptElement implements SVGURIReference;
A DOM consumer can use the hasFeature of the DOMImplementation interface to determine whether the SVG zoom event set has been implemented by a DOM implementation. The feature string for this event set is "SVGZoomEvents". This string is also used with the createEvent method.
The zoom event handler occurs before the zoom event is processed. The remainder of the DOM represents the previous state of the document. The document will be updated upon normal return from the event handler.
The UI event type for a zoom event is:
interface SVGZoomEvent : UIEvent {
readonly attribute DOMRectReadOnly zoomRectScreen;
readonly attribute float previousScale;
readonly attribute DOMPointReadOnly previousTranslate;
readonly attribute float newScale;
readonly attribute DOMPointReadOnly newTranslate;
};The specified zoom rectangle in screen units.
The DOMRectReadOnly object is read only.
The translation values from previous zoom operations that were in place before the zoom operation occurred.
The DOMPointReadOnly object is read only.
The translation values that will be in place after the zoom operation has been processed.
The DOMPointReadOnly object is read only.